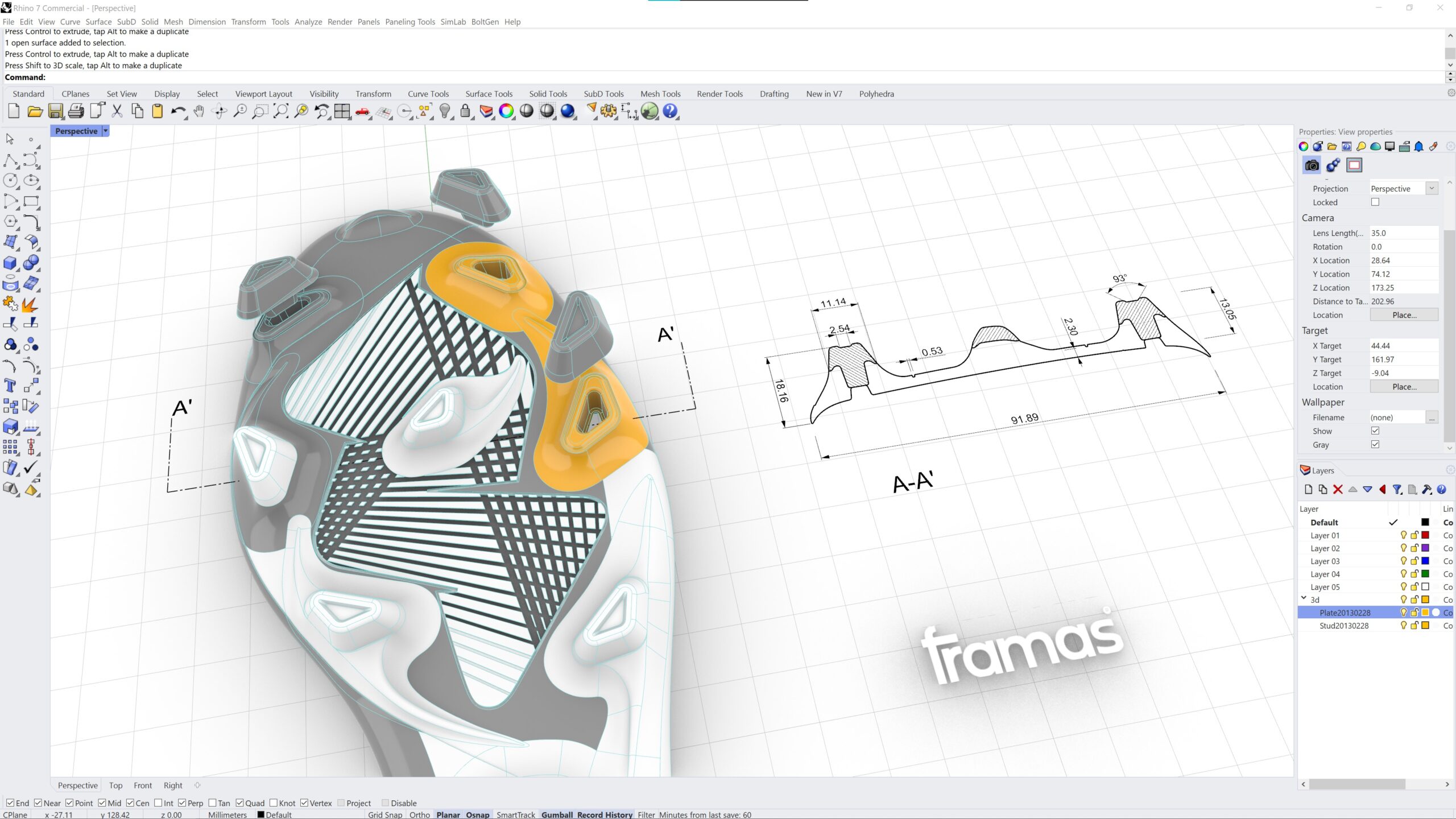
Laceless Challenge 2023
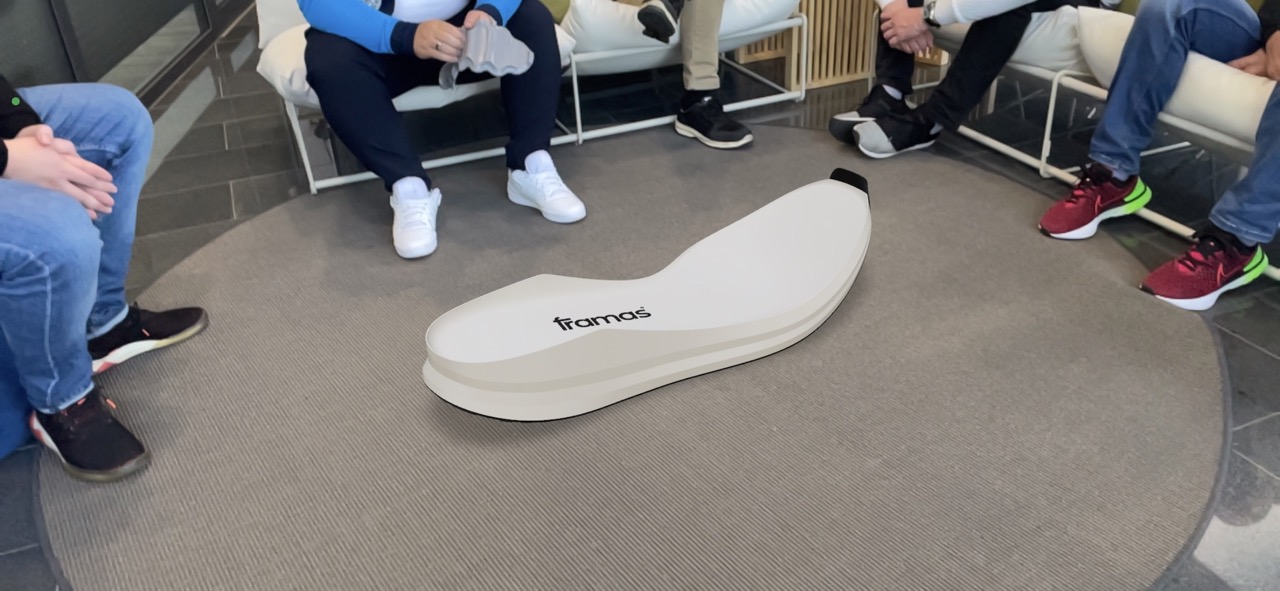
The Laceless Challenge is ongoing! We as framas would like to contribute our part and developed a women soccer last, which can be used by all participants to create a shoe.
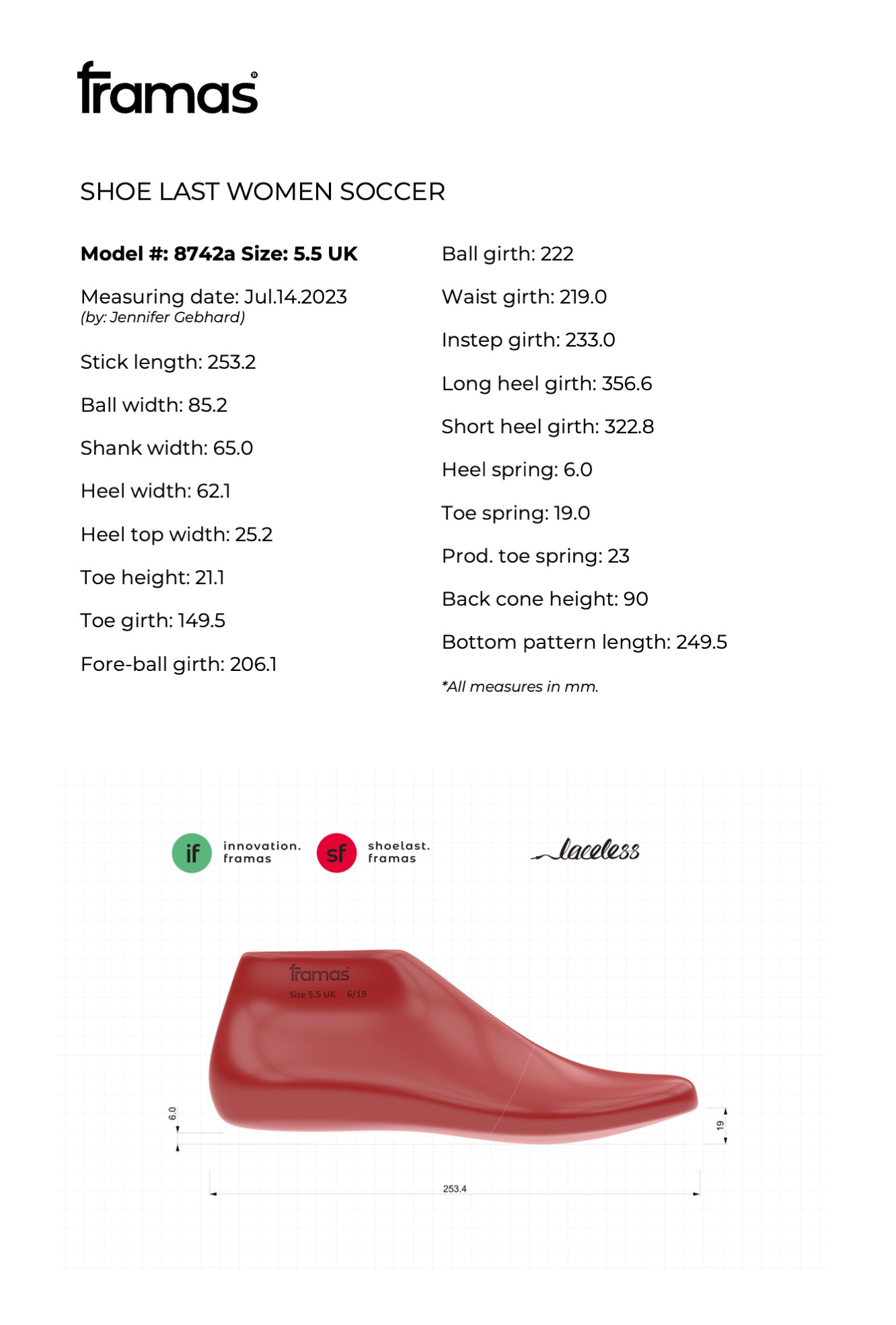
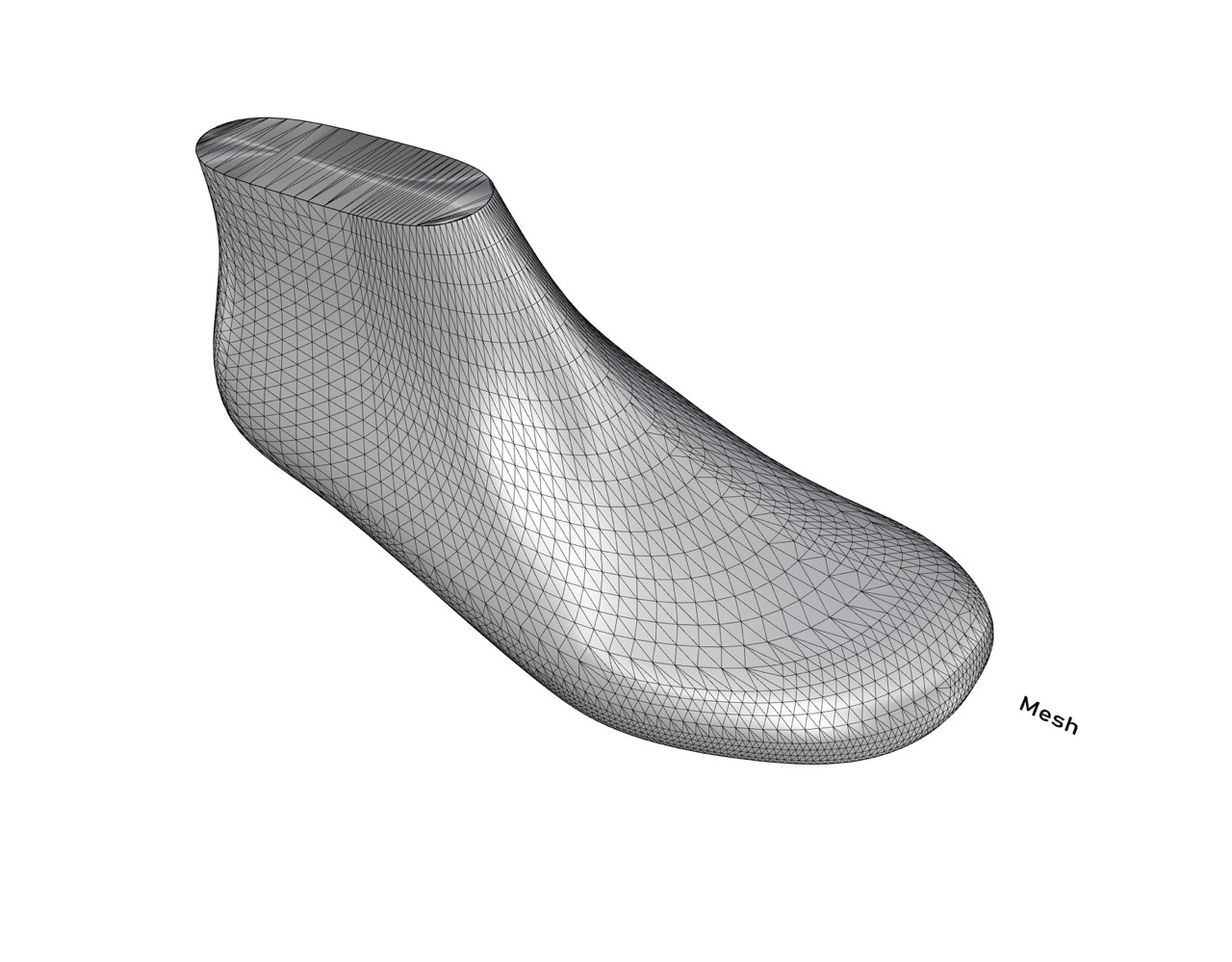
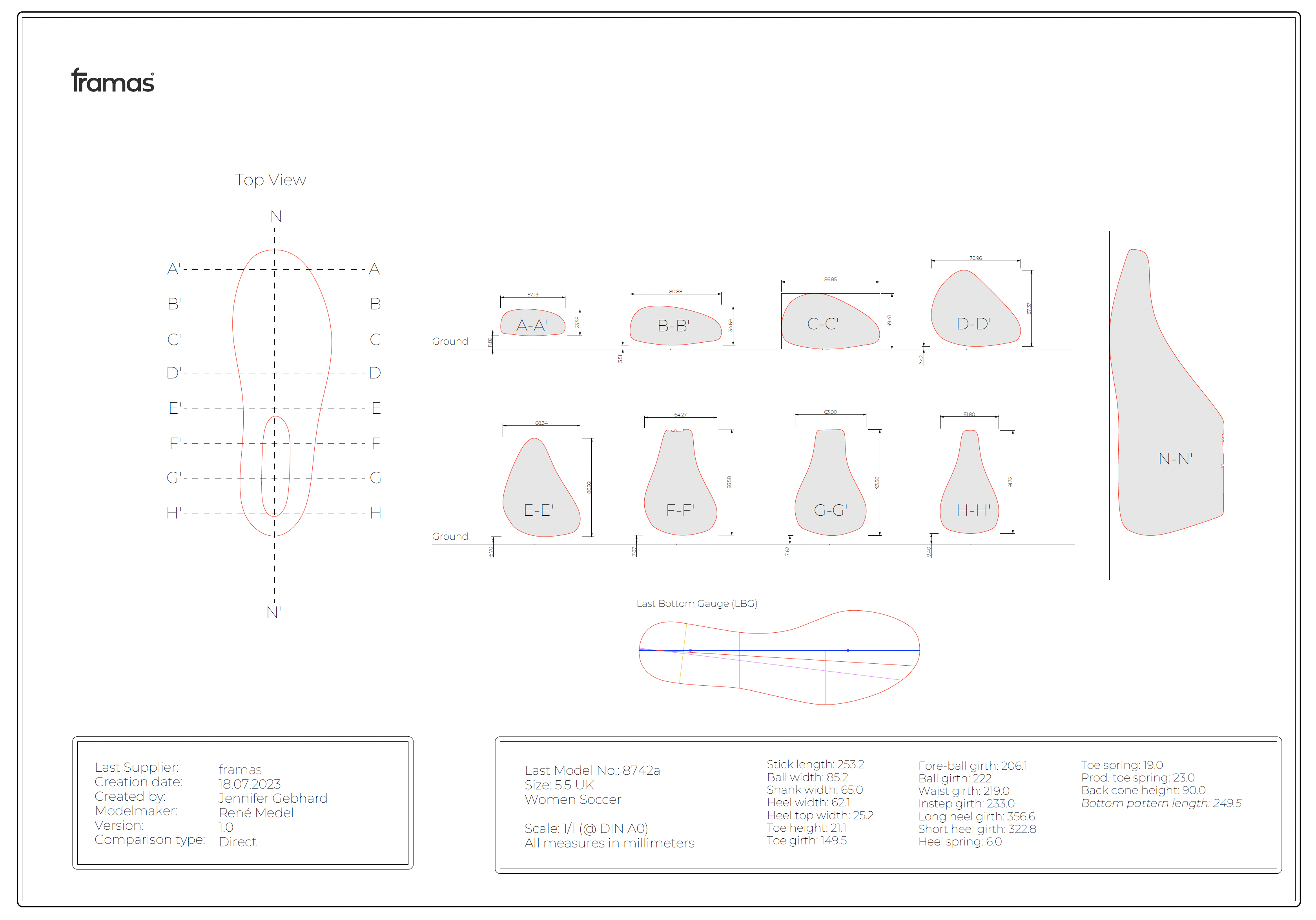
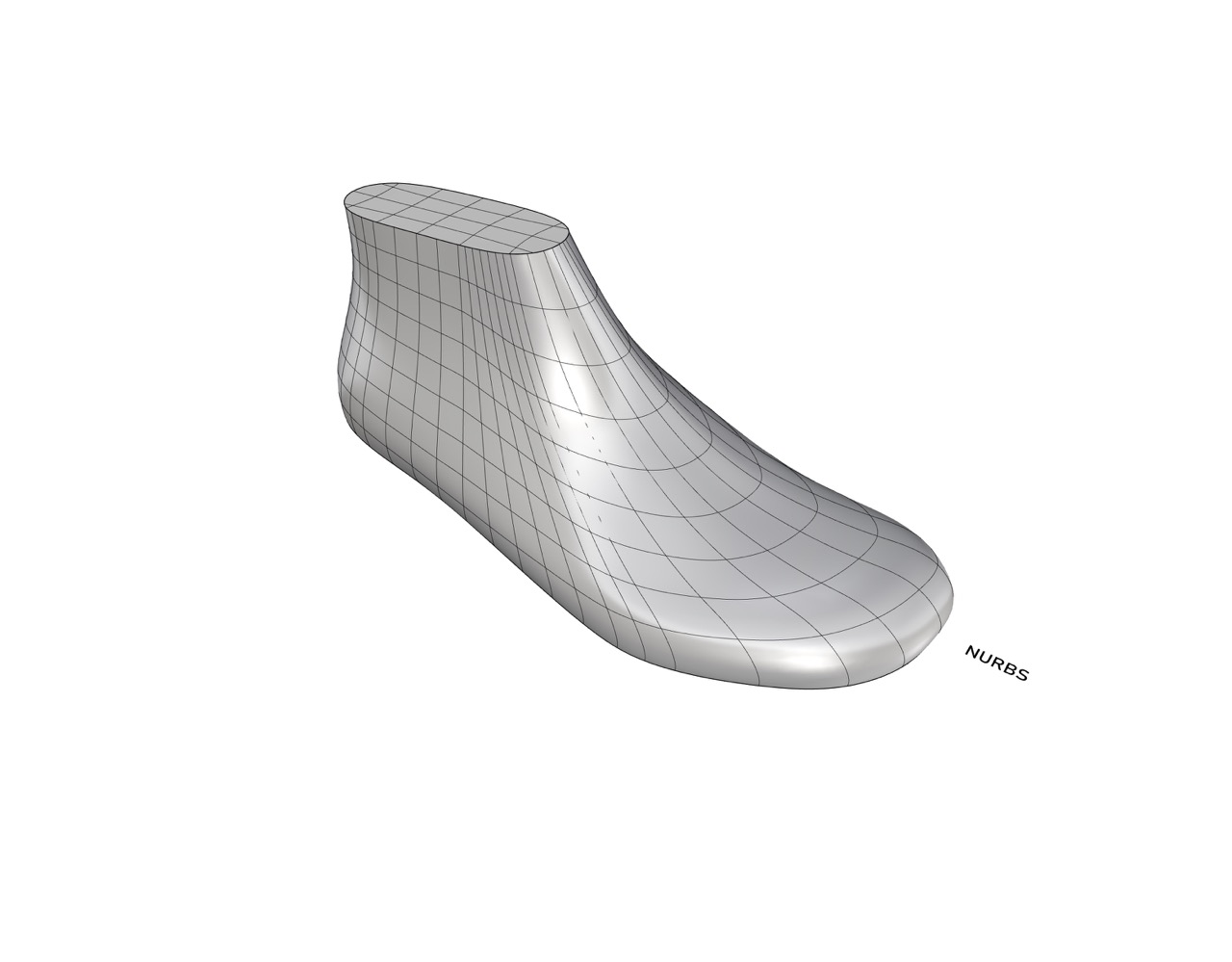
Women Soccer Last
Good luck to all designers of the Laceless Challenge 2023. #lacelesschallenge
Please feel free to use this women football 3D last we developed.
Size: 5.5 UK
Toe Spring: 19.0mm
Heel lift: 6.0mm
Ball girth: 222.0mm
Access the 3D files of the shoe last here:
If you would like to know more about the production and measurements of a shoelast, make sure to check out our blog article.
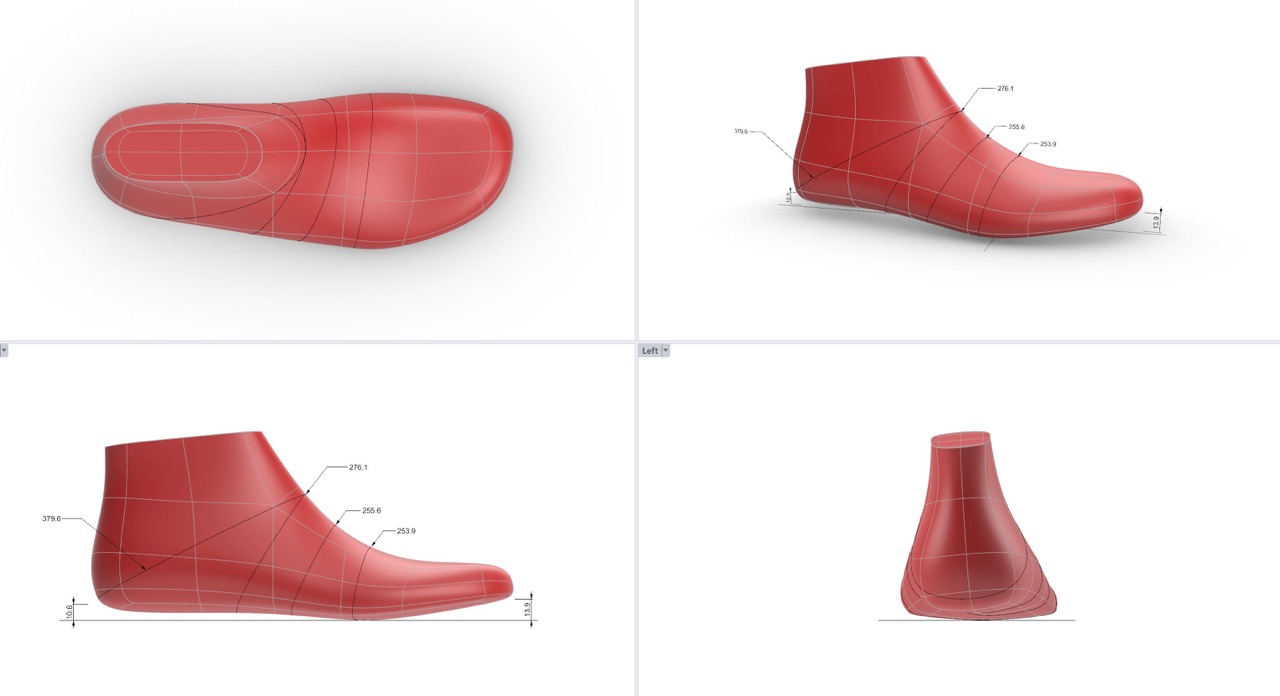
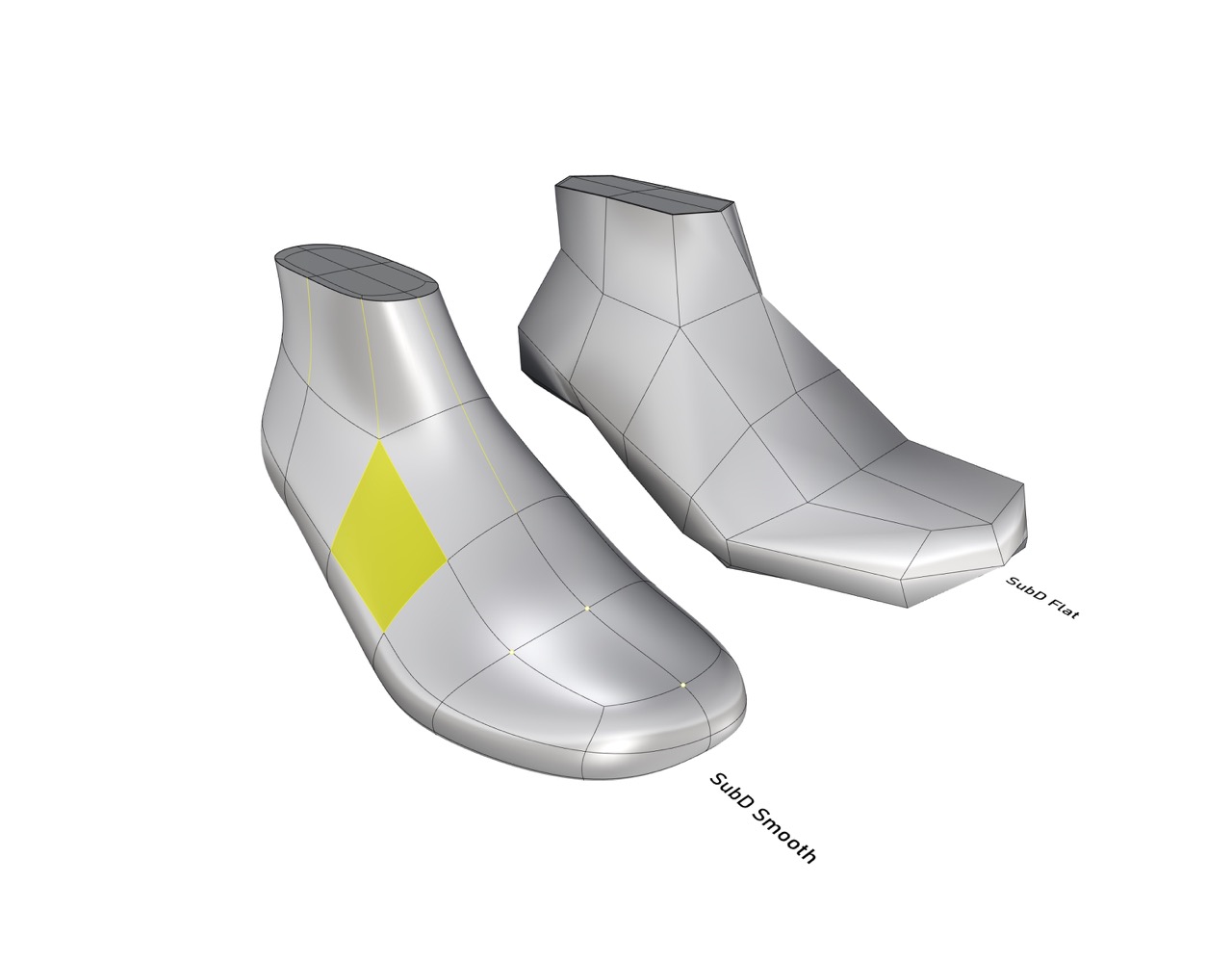
Football Last
A football shoe needs to sit tight on the foot. Therefore, a last for this category must have a narrow heel clip, a slim forefoot area and arch.
These functions provide extra stability for the whole foot and give a better connection to the football. As well the side walls of the last are rounded which makes it easier to handle the football. A football shoe must be comfortable as well because the players run a lot.
Difference Men & Women Football Last
A women football last is in total tighter in the forefoot area. The heel form of the women football last is rounder and more curved.
In general football shoelasts contain more running shoe elements than in earlier times.
Make sure to follow our Social Media channels. You can contact us anytime via LinkedIn, Instagram & Facebook. We are happy to receive any feedback.
Thanks for checking out our blog!




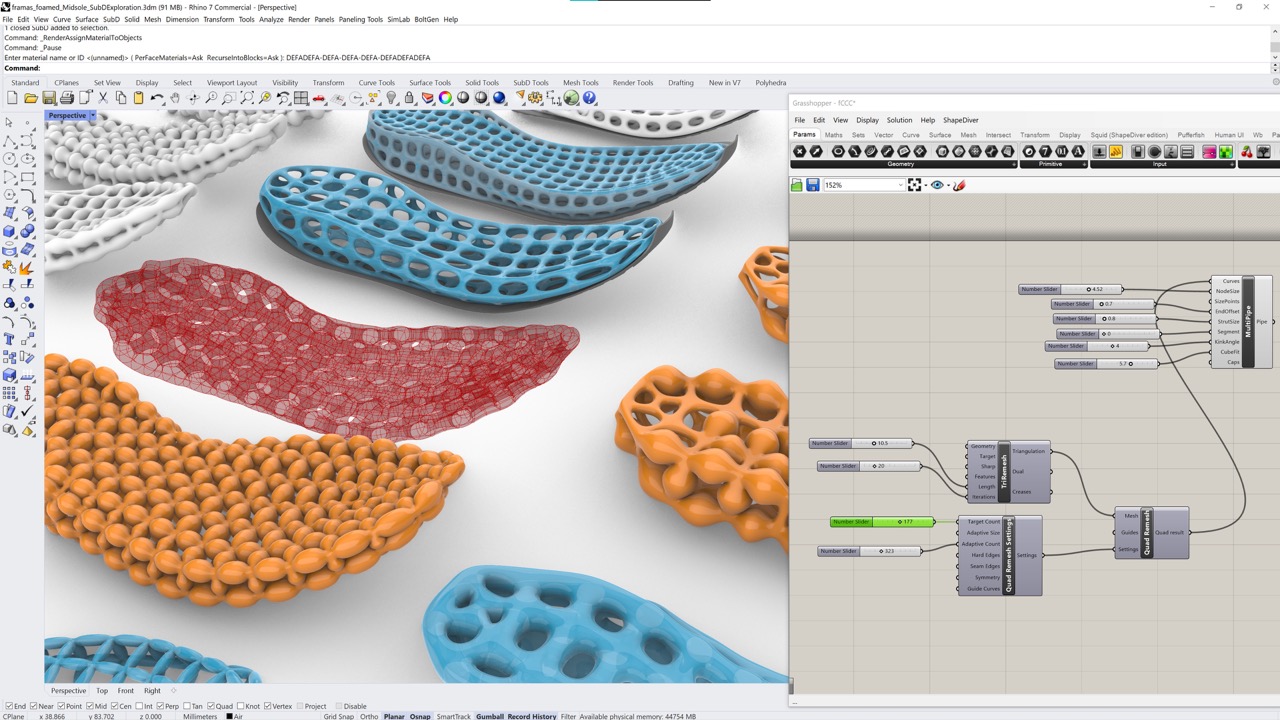
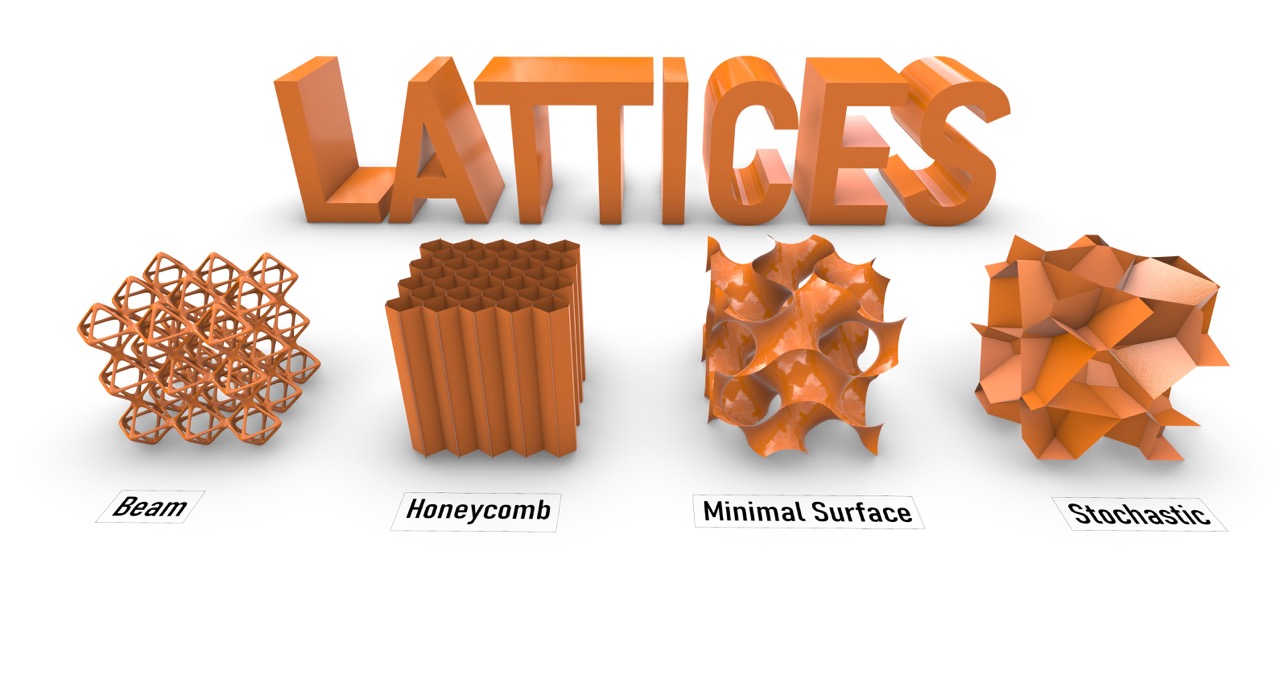
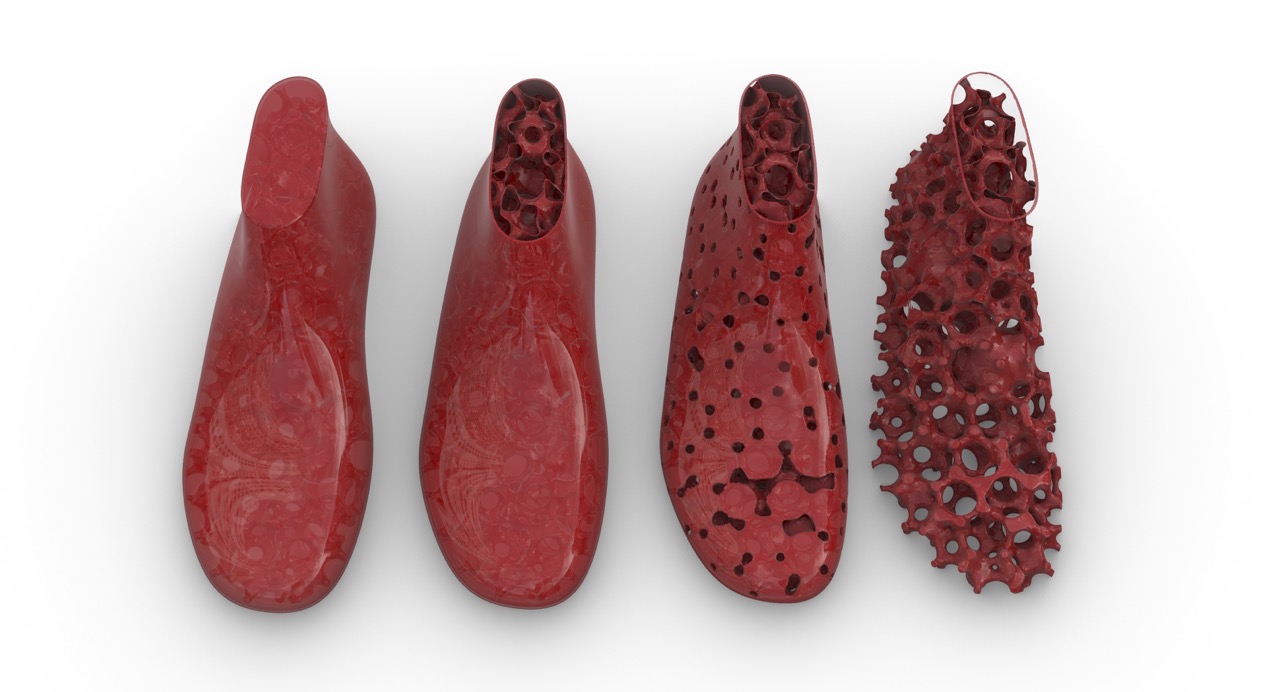




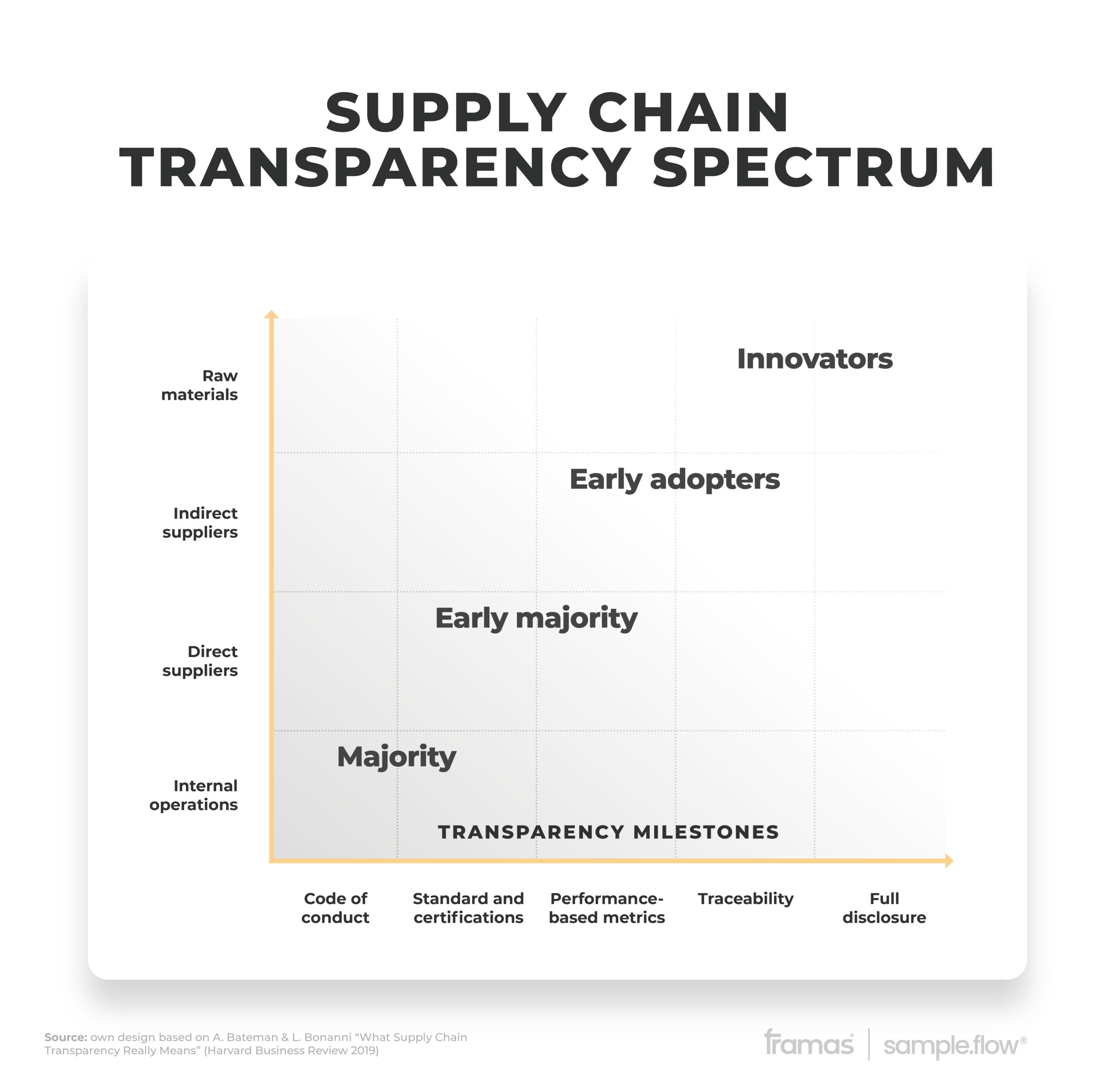




Neueste Kommentare