3D modelling has become an integral part of the footwear design process in recent years. It allows designers and developers to create and visualize their designs in a virtual environment, allowing for greater accuracy, efficiency, and innovation. In this blog article, we will dive into 3D modelling and its importance in footwear design.
Navigation
What is 3D modelling?
Why is 3D modelling important in footwear design and development?
What is the best 3D modelling approach for footwear design and development?
· NURBS
· Polygonal Meshes
· Polygonal Subdivision
Generative Design
Lattice & Additive Manufacturing
· Lattice Structures
· Additive Manufacturing
Extended Reality & Artificial Intelligence
· Extended Reality
· Artifical Intelligence
Summary
What is 3D modelling?
3D modelling is the process of creating a three-dimensional representation of a physical object or scene using specialized software. 3D modelling software allows designers to create a virtual representation of a shoe, from the sole to the upper, but also creates a base information to share with 3D Printing and later with development (Inline) for production.
3D modelling software allows designers to create and manipulate virtual 3D objects, such as shoe lasts, sole units, components, and reinforcements using a variety of tools, in particular shape and form manipulators, texture mapping, and lighting controls. It gives designers greater control and flexibility over the design process. In this blog article, we will dive into what 3D modelling is, its benefits, and its applications in the footwear industry.
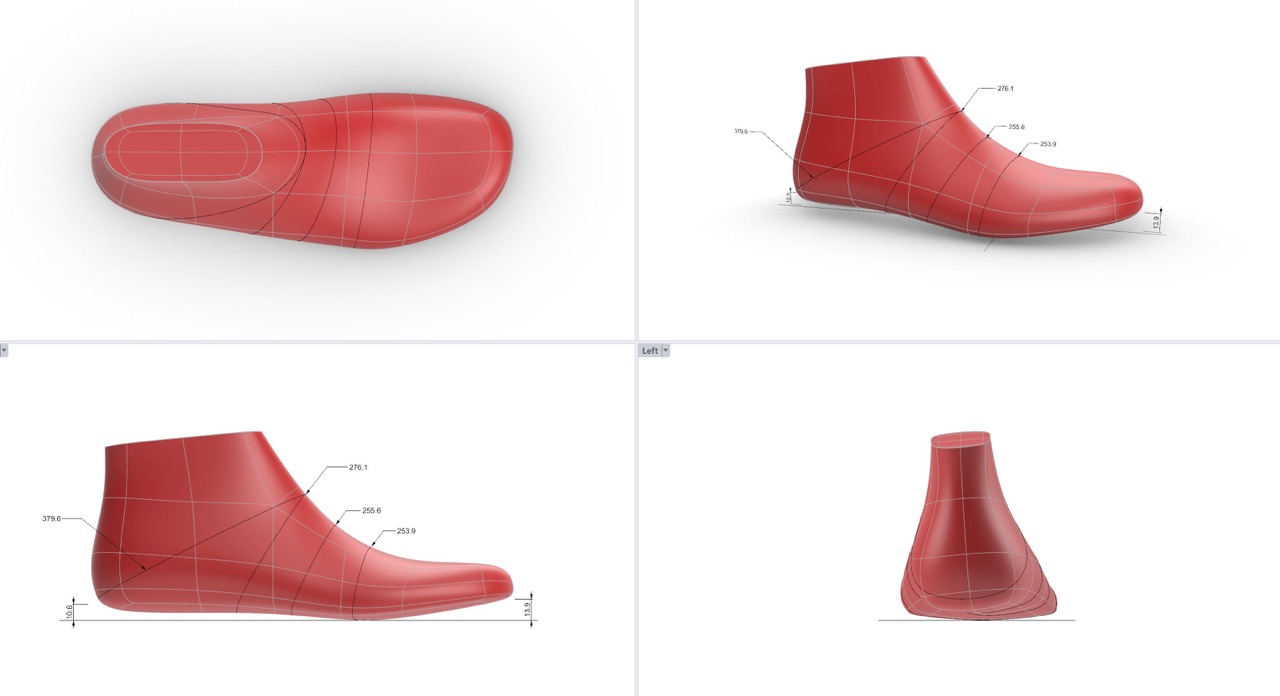
Why is 3D modelling important in footwear design and development?
3D modelling is a powerful tool for footwear designers, offering increased speed, accuracy, and visualization capabilities. By adopting this technology, designers can create better products, faster, and with greater efficiency.
1. Greater accuracy and efficiency: 3D modelling software allows designers and developers to create a precise and accurate representation of a shoe before it’s even produced. This reduces the need for traditional sketching and physical prototyping, which can be time-consuming and expensive. The ability to quickly create and modify designs also allows footwear brand creation teams to work more efficiently, consistently, with improved quality and on time.
2. Enhanced collaboration: With 3D modelling, designers and developers can share their designs with team members and stakeholders in a virtual environment. This makes it easier for designers to collaborate and receive feedback, even if team members and factory partners are located in different parts of the world.
3. Innovation and creativity: 3D modelling software like Rhinoceros allows designers to explore new designs and push the boundaries of traditional shoe design. With the ability to create complex shapes and textures, designers can experiment with new materials and construction techniques, leading to the creation of innovative and unique shoe designs.
4. Improved visualisation and communication: 3D models can be easily shared and viewed from multiple angles, making it easier for designers, developers, engineers, shoe factory partners and other stakeholders to visualize and understand the design. This can help facilitate communication and collaboration throughout the design, development and production process.
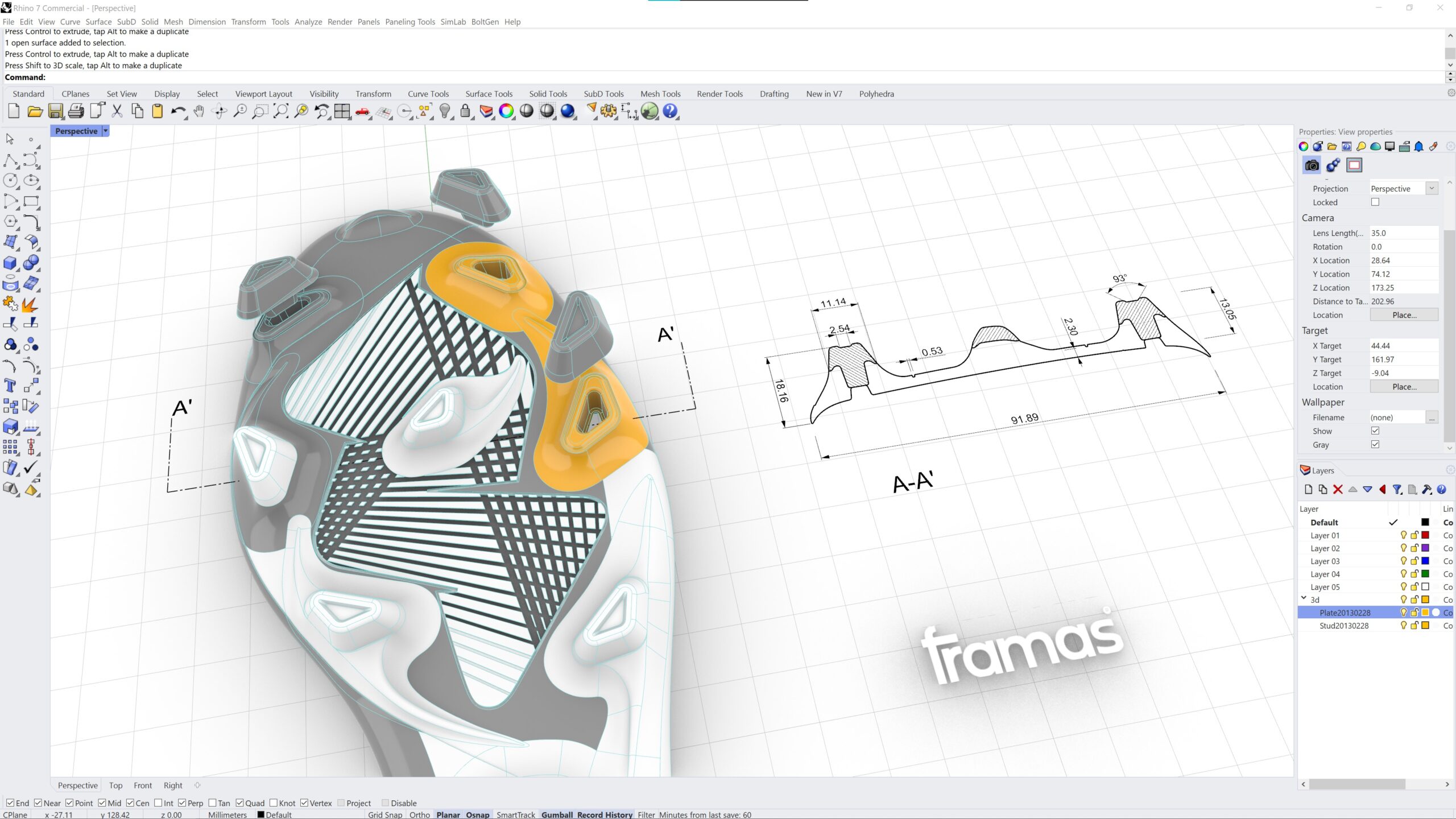
3D modelling has a wide range of applications in footwear design and development, including:
1. Concept development: 3D modelling can be used to quickly create and refine new design concepts, allowing designers to explore different ideas and variations before committing to a final design.
2. Tech packs: 3D models can be an efficient part of a tech pack. Footwear developers share tech packs with their shoe factory partners to give instructions on how to develop and manufacture the model. 3D Models have a much higher informative level if they include 360-degree 3D models of computer-aided design (CAD), shell pattern, tooling layering, measurements and upper layering. Particularly, showing the CAD in all its 5 typical views (lateral, medial, top view, outsole view, and heel view) becomes obsolete if it can be substituted by a single 3D model.
3. Prototyping: 3D models can be used to create physical prototypes using 3D printing or other rapid prototyping methods. This can help designers and developers to test and refine their designs before committing to mass production.
4. Production: 3D models can be used to create production-ready designs and tooling, which can help ensure consistency and quality in the final product.
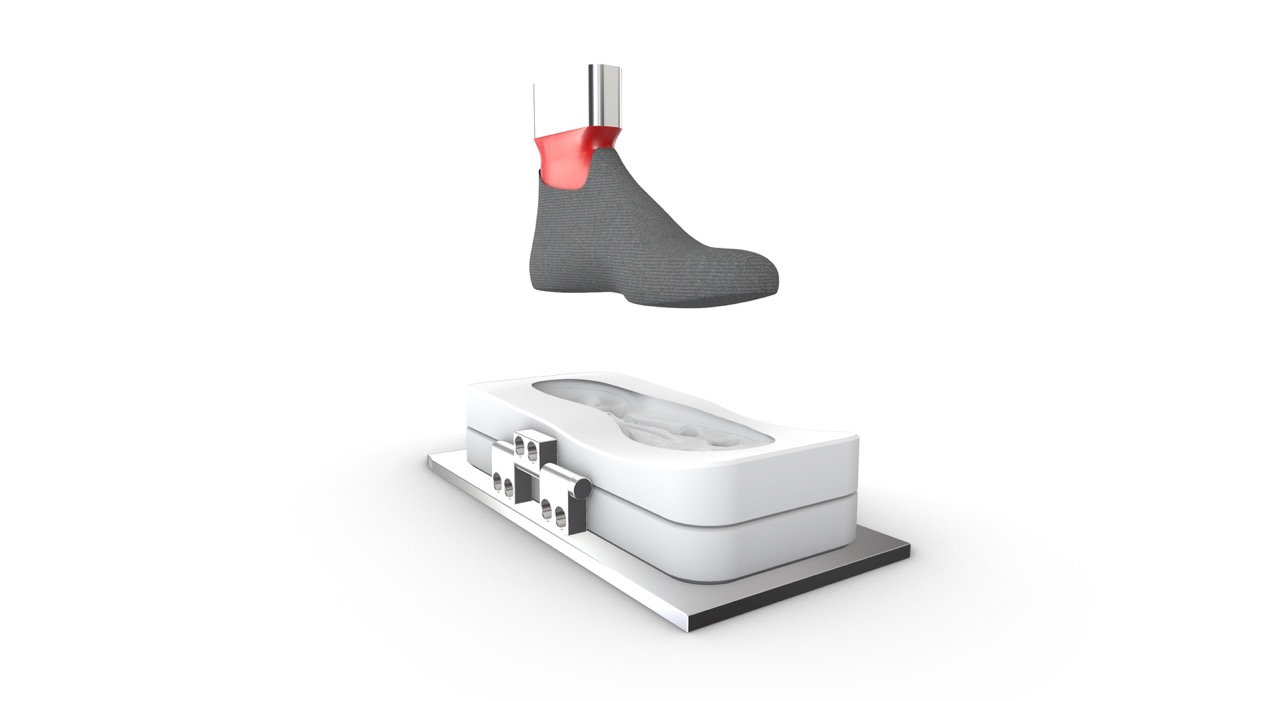
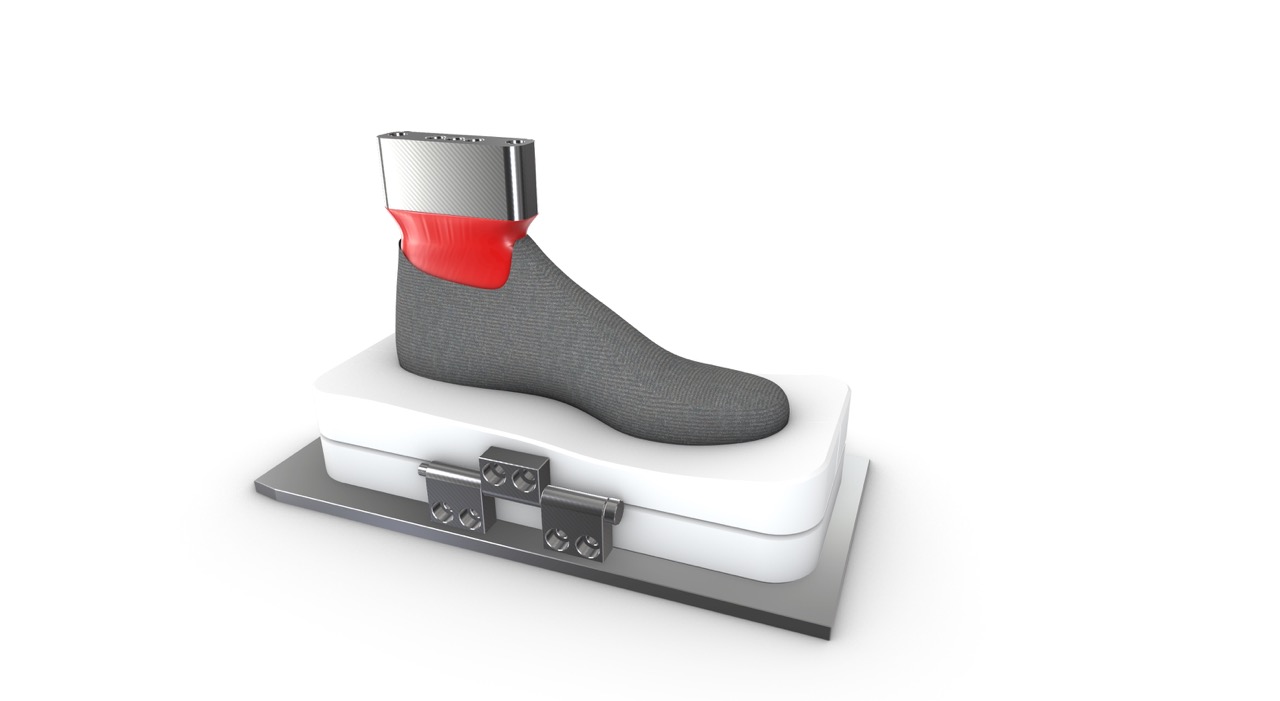


What is the best 3D modelling approach for footwear design and development?
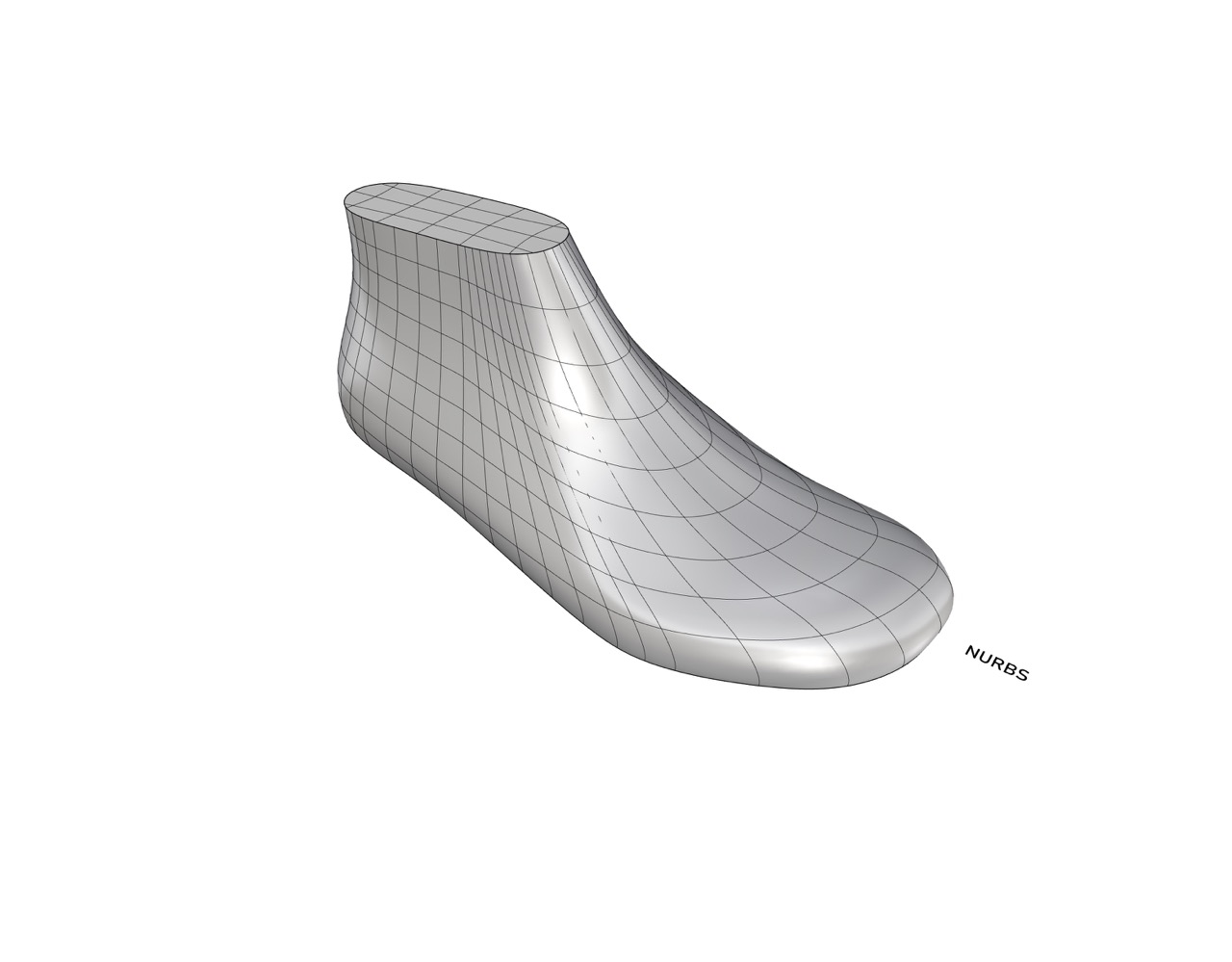
1. NURBS
NURBS (Non-uniform rational basis spline) is a mathematical representation of 3D geometry that is widely used in computer-aided design (CAD) applications. NURBS surfaces are defined by control points and curves, which are used to define the shape of the surface. NURBS surfaces are highly accurate and can be manipulated with precision, making them ideal for modelling complex shapes and curves. Some of the key features and benefits of NURBS for footwear modelling include:
1. Highly accurate surfaces: NURBS surfaces can be precisely controlled, allowing for accurate modelling of complex shapes and curves.
2. Smooth surfaces: NURBS surfaces can be smoothed and refined, resulting in highly polished and visually appealing designs.
3. Efficient workflow: NURBS surfaces can be easily edited and modified, allowing for an efficient workflow and faster design iterations.
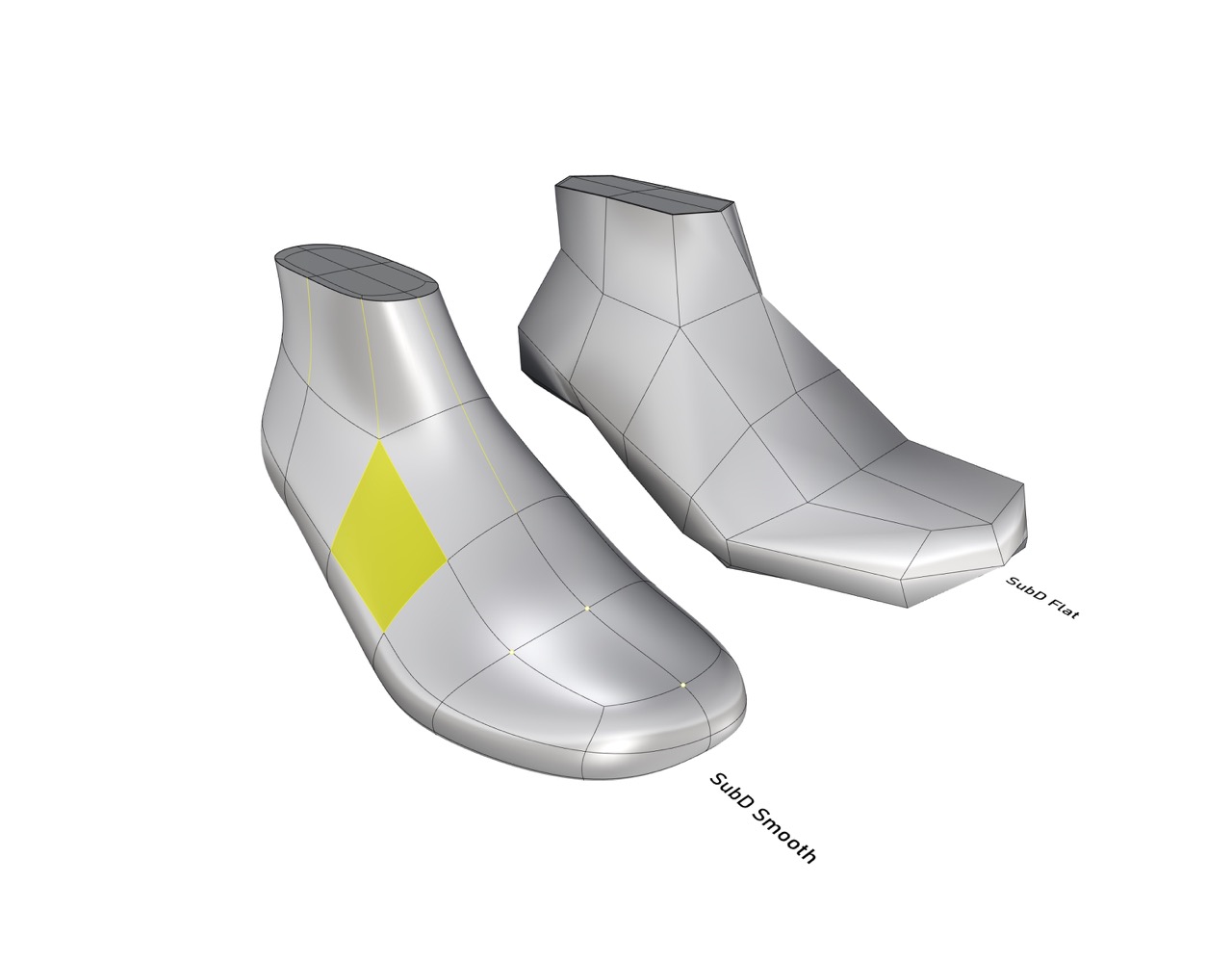
Meshes are a popular approach to 3D modelling that involves representing 3D geometry as a series of interconnected polygons (triangles and/or quads). Polygonal meshes are widely used in gaming and animation but are also used in footwear design. All the models we use for 3D printing, are Meshes.
Some of the key features and benefits of polygonal meshes for footwear modelling include:
1. Versatility: Meshes can be used to create a wide range of shapes and designs, making them highly versatile.
2. Realistic textures: Polygonal meshes can be textured and shaded to create highly realistic and detailed designs.
3. Large amount of polygons: Meshes are not that easy to manipulate and edit, since they are made of many polygons, and usually requires to repair the geometry, to have all the polygons and vertices connected.
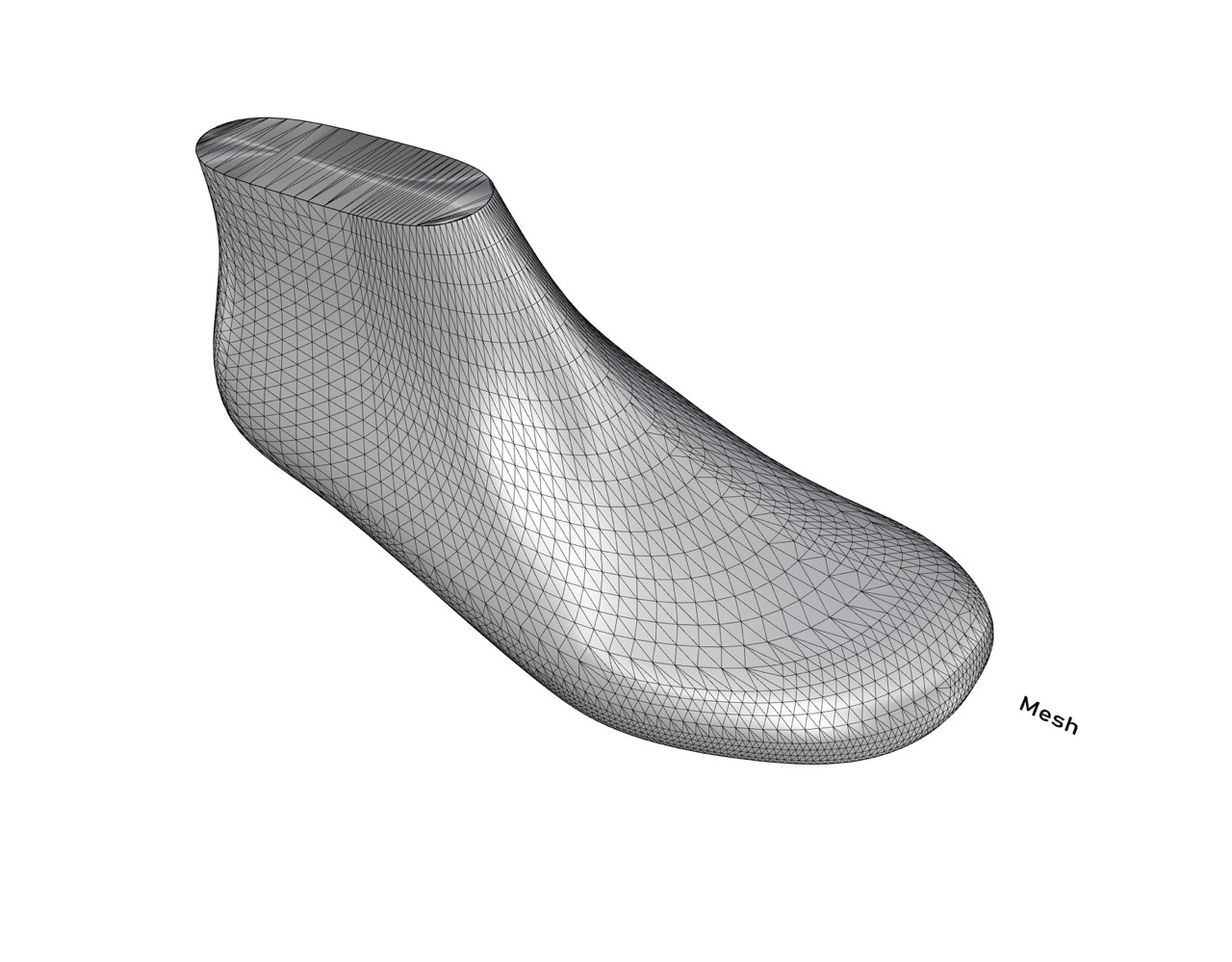

Polygonal Subdivision (SubD) is a type of polygonal mesh (low polygons) that is used to create smooth, organic shapes utilizing algorithms like Catmull-Clark commonly used for 3D animation industry since 1978. SubDs are defined by a set of faces, edges and vertices that can be moved and adjusted to create complex shapes. Some of the key features and benefits:
1. Smooth surfaces: SubD can be smoothed and refined, resulting in highly polished and visually appealing designs.
2. Organic shapes: This topology is ideal for creating organic shapes curves, such as those found in sport footwear.
3. Efficient workflow: SubD geometries can be easily edited and modified, allowing for an efficient workflow and faster design iterations.
Generative Design
Generative Design is an innovative approach to 3D modelling that uses algorithms to create complex designs almost automatically. By inputting design criteria such as shapes, geometric rules, and performance specifications; Generative Design software (like Grasshopper) can generate multiple design options (iterations) quickly and efficiently. This technology also named Algorithmic Modelling, has many potential benefits for the footwear industry, including:
1. Faster design iteration: Generative design allows footwear designers to create and evaluate multiple design options quickly and easily. This can help reduce the time and cost of the design process, while also enabling designers to explore more creative and innovative design solutions.
2. Improved design quality: Algorithmic modelling algorithms can take into account a wide range of design parameters, such as materials, geometries, mechanical properties, loads, and performance requirements. This can help ensure that the final design is optimized for its intended use, with improved functionality and performance.
3. Enhanced customization: Generative design can also be used to create highly customized footwear products tailored to the specific needs of individual customers. By inputting personalized data such as foot shape and size, generative design algorithms can create unique designs that are optimized for the individual’s needs.
4. Increased sustainability: It can also help reduce waste and promote sustainability in the footwear industry. By optimizing designs for materials and manufacturing processes, generative design can help reduce the amount of material waste and energy used in the production process. (You want to learn more about other ways to promote sustainability? Check out our blog post about green materials here.)
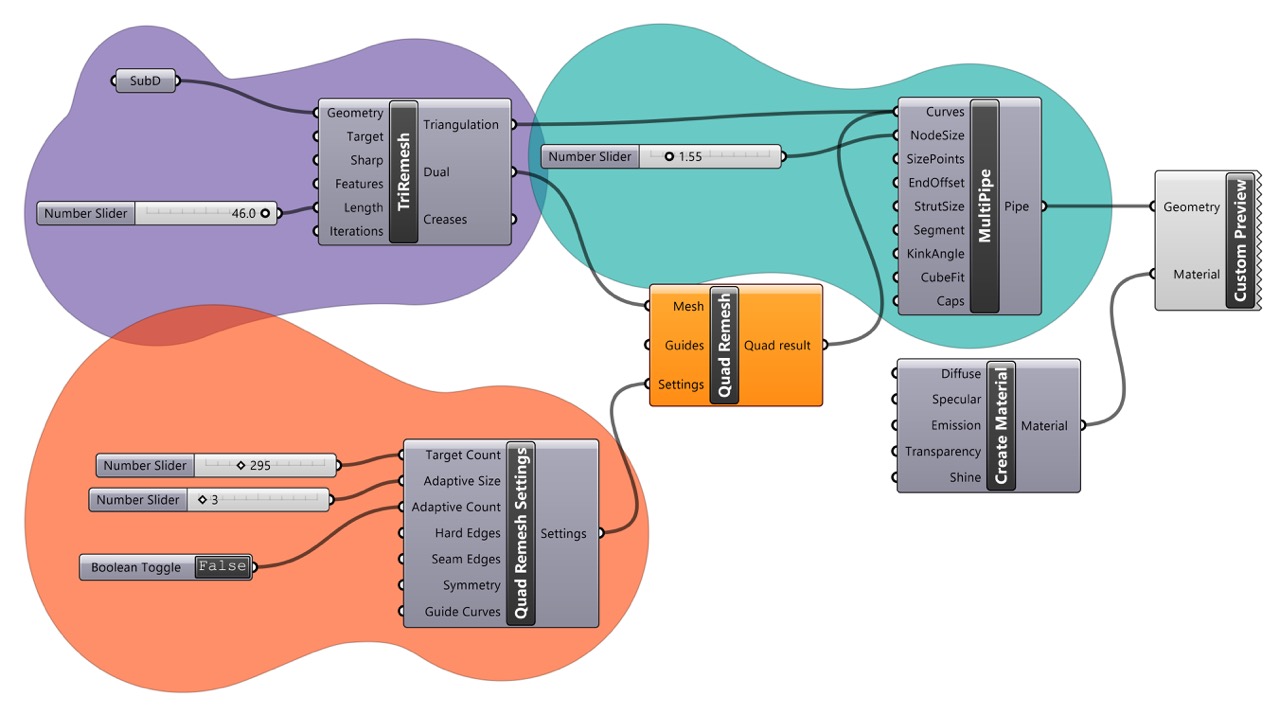
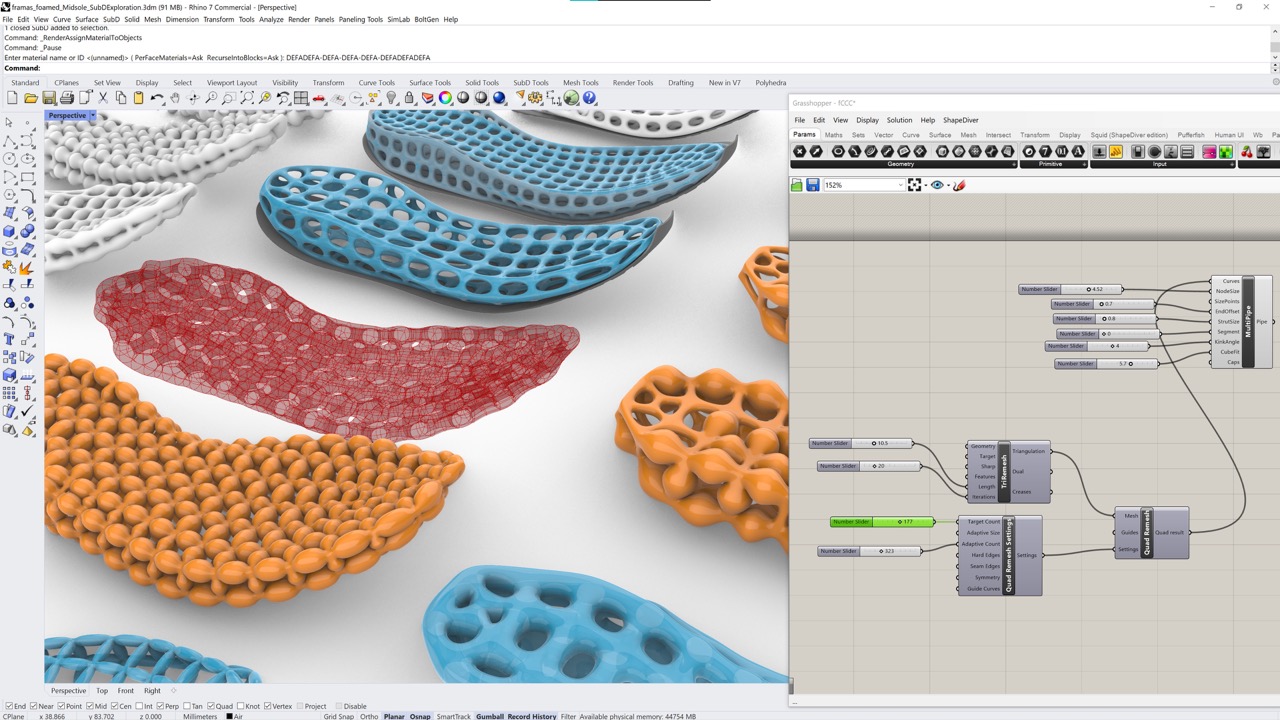
Lattice & Additive Manufacturing
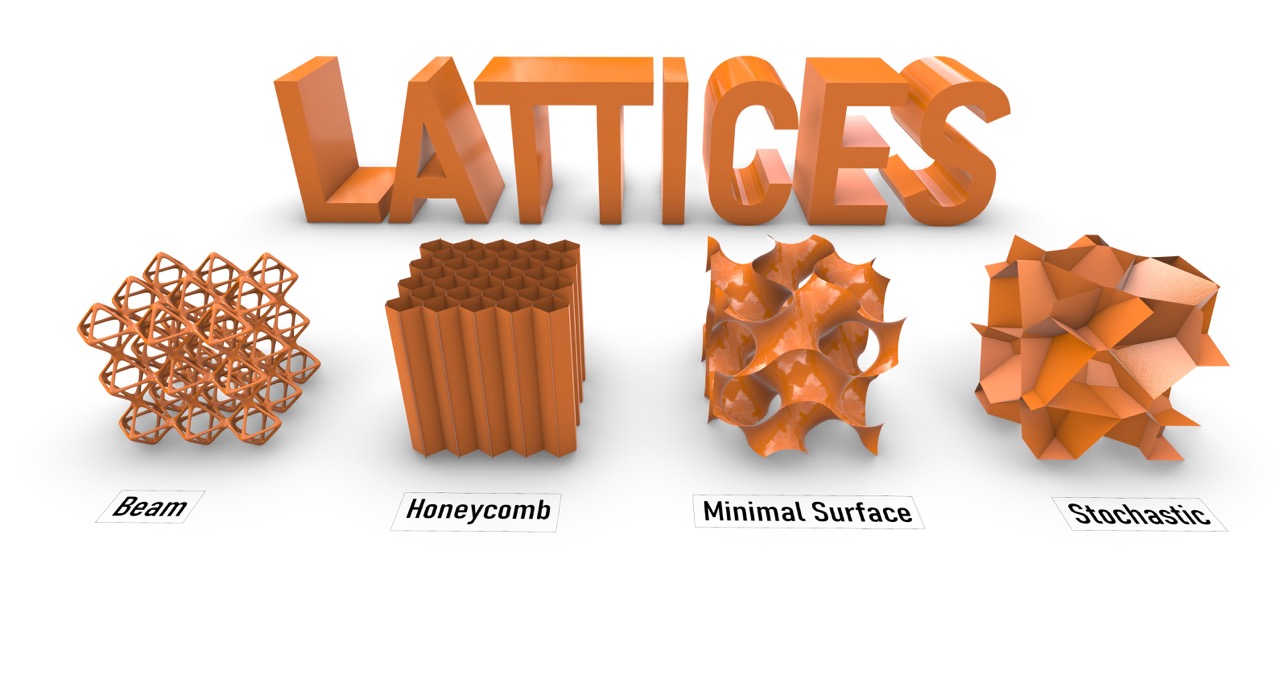
1. Lattice Structures
2. Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing (AM) is the part of the Industry 4.0 which uses different technologies commonly named 3D printing. This is a process by which a three-dimensional object is created from a digital model. 3D printing technology has advanced significantly in recent years, allowing for the creation of highly complex and detailed objects, including footwear products. By using 3D printing in footwear design, designers can create prototypes and even finished products quickly and efficiently, with a high degree of accuracy and precision and using several types of materials.
By combining lattice structures and 3D printing, footwear designers can create highly complex and customized designs that are optimized for specific performance requirements. For example, designers can create lattice structures that are tailored to specific pressure points on the foot, or that are optimized for specific types of movement or activity. These lattice structures can then be 3D printed using a range of materials, including plastics, metals, and even bio-based materials, to create highly functional and sustainable footwear products.
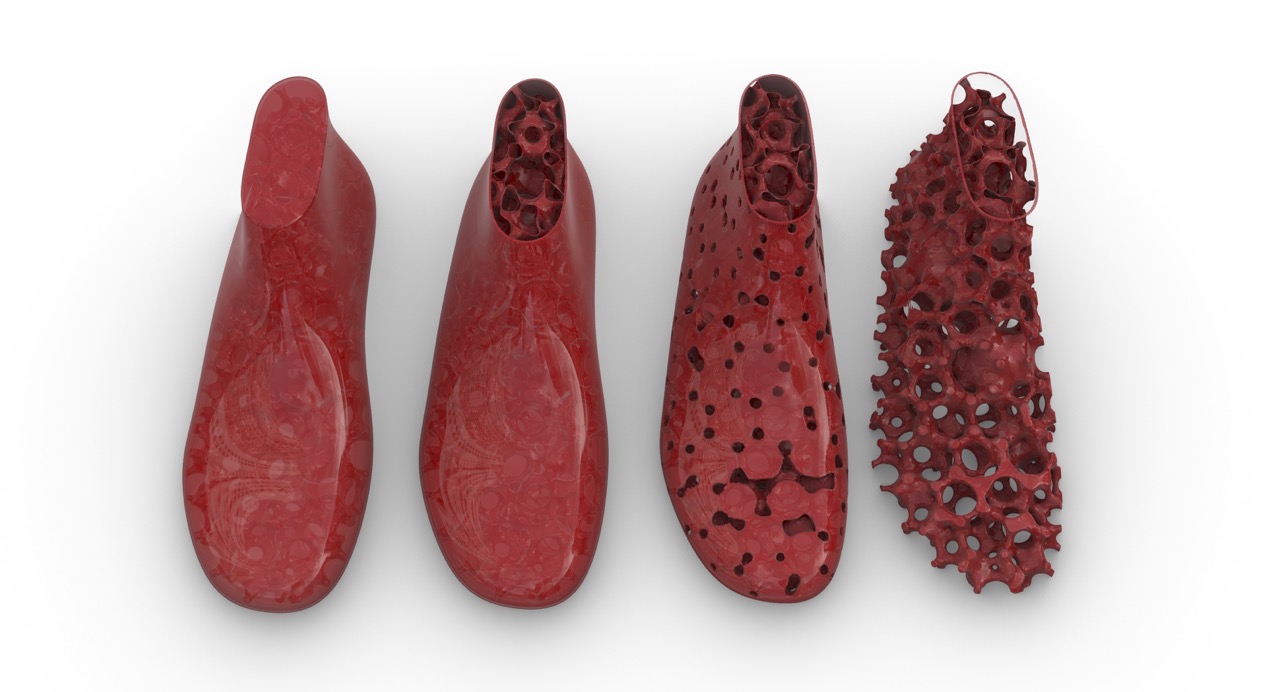
Extended Reality & Artificial Intelligence
1. Extended Reality
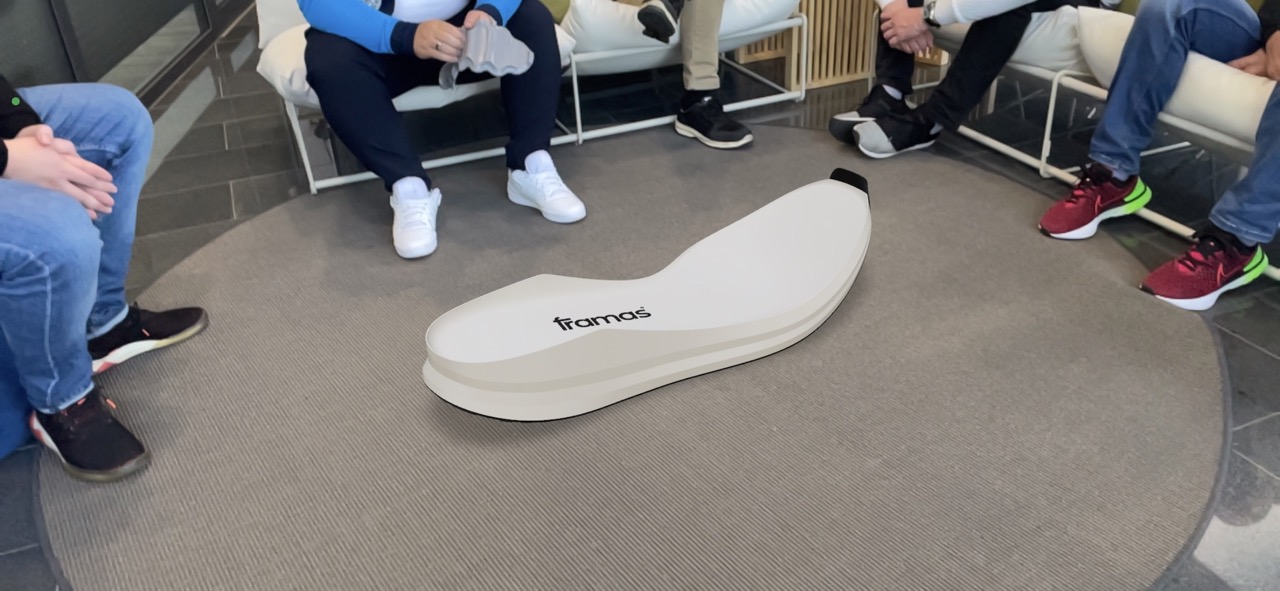
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses a range of technologies, including Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). XR technologies are being used in the footwear industry in a variety of ways, including:
1. Design: XR technologies can be used to create immersive design environments that allow designers to explore and refine their designs in a virtual space.
2. Prototyping: XR technologies can be used to create realistic virtual prototypes that can be tested and refined before physical prototypes are created.
3. Retail: XR technologies can be used to create immersive shopping experiences that allow customers to try on and customize footwear products in a virtual environment.

2. Artifical Intelligence
Artifical Intelligence is another technology that is being increasingly used in the footwear industry. AI is being used to:
1. Improved design creation and ideation: Large Language Models (LLM) can be used to analyze customer data and feedback to inform design decisions and create personalized footwear products.
2. Optimize production: AI can be used to optimize production processes and improve supply chain management, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
3. Enhance marketing: Text-to-Image and Image-to-Image can be used to analyze customer data and behavior to create targeted marketing campaigns and improve customer engagement.
4. Better understanding of the market and consumer behaviour: AI could help us to know more about Intellectual Properties (IP) rights and patenting of concepts, before turning them into products. Brands and consumer data are also easy to reach, using the right prompts.

In summary, 3D modelling has revolutionized the way footwear designers approach their work, providing them with a range of powerful tools and technologies to create innovative and functional shoe designs.
Advancements in technology, such as Extended Reality, Artificial Intelligence, Generative Design, Lattice structures, and 3D printing have transformed the way designers and developers work. There are several approaches to 3D modelling for footwear design, each with its own features and benefits.
If you would like to learn more from René, make sure to also check out the webinar he did with McNeel Europe.
If you liked this article, make sure to follow our Social Media channels. You can contact us anytime via LinkedIn, Instagram & Facebook. We are happy to receive any feedback and tell us what other topics are of interest to you. We will try to address them in the near future.
Thanks for checking out our blog!
